Nutrition
Muscle Building Breakfast Ideas: Start Your Day Right
Muscle Building Breakfast Ideas is the most important meal of the day and there are no excuses for skipping it, especially when you are trying hard to put on muscle mass or increase strength. Regardless of how late you get up, you should always make time for a rich breakfast to fuel your body and prevent it from using muscles for energy.
Since the body’s most preferred source of energy is a carbohydrate, you have always make sure that before getting engaged in a high or medium physical activity you do eat something. Below you will find some great muscle-building breakfasts ideas that will not keep you long in the kitchen but are full in carbs and protein to provide with enough energy for whatever day may hold.
Morning Smoothies For Bodybuilders
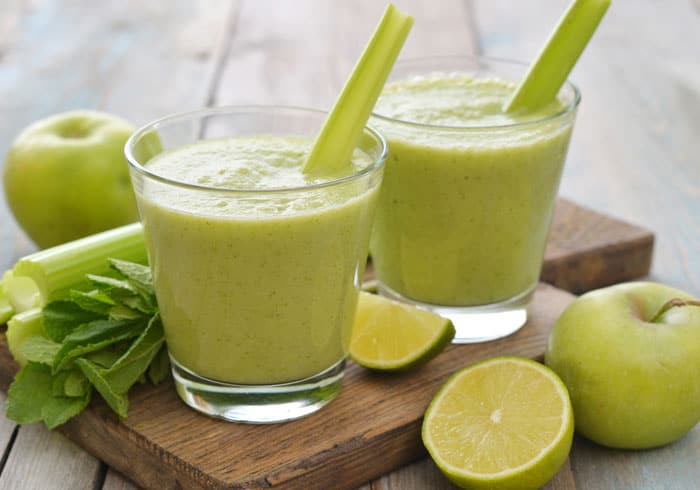

One of the best idea of breakfast for all bodybuilders -- easy to do, very conventional and with amazing nutritional properties. Make the base whey protein (50 gr of it is quite enough) and add in any fresh or dried fruit you like. If you are of those persons who can’t face food first thing in the morning, then a smoothie is definitely your way to go.
Yogurt
Over 61% of skeletal muscle is glutamine, an amino acid that reduces muscle breakdown and improves protein absorption rate. What has it in common with yogurt and dairy products? Wait to find it out.
Our body produces glutamine, but in order to speed up recovery supplementation with the right food is required, such as chicken, beef, fish, and eggs.
The problem is that during cooking much of glutamine is lost, that’s why including low-fat dairy products in your morning routine would yield lots of benefits.
Stick with Cereals
To boost the carbs in your morning, add a portion of oatmeal mixed with blueberries, flaxseeds or nuts. Blueberries have been proved to hasten muscle recovery after a workout, while flaxseeds and nuts are rich in protein and Omega-3, which greatly improve protein synthesis.
Whether you decide to eat cereals cooked or uncooked, the most important to make room for them in your breakfast routine for at least several times a week. And, if possible, avoid instant cereals and stick with integral whole grain oatmeal.
Eggs and Meat

One of the superfoods for building muscle mass that’s a great fit for your morning breakfast. Rich in lean protein, white eggs are not only delicious but the perfect meal before or after a morning workout. Do you know how many calories&protein is found in a white egg? Almost 20 calories, 4gr of protein and just 0.06 fat.
No need to say that meat is also a great source of protein which can be easily incorporated into your morning meal. Have a breakfast sandwich with chicken breast tossed in eggs to boost your protein level for the whole day. Read the Right Food Before And After Workout to understand what foods are best to eat get the most of the gym and help muscles to recover in the shortest time.
Vegetable And Fruits
Rich in carbohydrates and vitamins, vegetables and fruits have to be one for your first choices in the morning. You may be prone to leave them for lunch or dinner or between in them, but it’s not the case.
Blend them with any source of protein and you can be sure that your breakfast is 100% nourishing and provides with all the ingredients needed for successful training in the gym.
Among vegetables, potatoes can be your pick as it is easy to cook, tasty and rich in carbs. Regarding fruits, then mango is a quick source of natural sugar, bananas are high in potassium, preventing muscle breakdown, avocado is rich in fiber, oranges are rich in vitamin A and vitamin C and a great source of potassium as well.
Raspberries are high in vitamin C and K, while pomegranate contains potassium, magnesium, fiber, and lots of vitamins, such as B-1, B-2, B-6, C, E, K.
Check these 5 Foods that Increase Testosterone before making your grocery shopping.
The Biggest No-Nos For Morning Meals

What products should you avoid eating in the morning even if you are in a rush? Some breakfast ideas for those trying to build muscle can be worse than others and have no benefits at all on your body. You gotta know this because the more educated you are in regard to healthy food choices, the better for you. Below are some breakfast ideas that TV and promotional have induced us they are what you need, but it is not so. See why.
Must Read: The Best Routine For Your Body Type
- Have a glass of orange juice. Store juices contain a lot of sugar, while the nutritional value is very low. The best will be to eat an orange and drink a glass of water - the whole fruit is not only richer in vitamins, but also provides with a lot of fiber that will tame your hunger.
- Pancakes, waffles or pastries. A big no for breakfast, if you really care about what you are feeding your body with. A healthy alternative is whole-grain cereals with different fruits, nuts or low-fat yogurt.
- Breakfast bars. They are high in calories but poor in so needed nutrients in the morning.
- Avoid coffee add-ons. Having a coffee in the morning is a healthy choice, but get rid of low-fat and artificial creamers and don't load it with sugar. Use cinnamon instead, which proved to reduce blood glucose and cholesterol.
Want to know what other mistakes bodybuilders do when it comes to their diet? Check these Common Dieting Mistakes you should make sure are not doing yourself.
Conclusion:
Make your first meal in the morning work for you. The above muscle building breakfast options are not only healthy but tasty and rich in protein, carbs, and vitamins -- all meant to sustain protein metabolism and recover. Get into a routine of having your breakfast regardless of the morning rush, because feeling full will help you stay away from foods with zero nutritional value.
Bodybuilding
Calorie Dumping: A Bodybuilder’s Guide

"Calorie dumping" in bodybuilding refers to a strategy where an individual consumes a large number of calories in a single meal, often following a period of low-calorie intake.
This practice is believed to support muscle growth by providing a surplus of energy and nutrients.
The idea is that after a period of restricted calorie intake, the body becomes more efficient at utilizing nutrients, making it more receptive to absorbing and utilizing the surplus calories in a short period.
However, this approach may not suit everyone and should be approached cautiously as it can lead to discomfort and potential digestive issues.
Calorie dumping, also known as refeeding or cycling calories, is sometimes preferred by bodybuilders to help prevent metabolic adaptation and aid in breaking through plateaus.
By occasionally consuming higher calorie levels, they aim to boost metabolism, replenish glycogen stores, and maintain hormone balance for better muscle growth and fat loss in the long term.
Bodybuilders focus on controlled nutrition plans to optimize muscle growth and minimize fat gain. However, occasionally, you might increase the calorie intake temporarily before an intense workout or competition to boost energy levels, but this isn't considered calorie dumping in the traditional sense.
ALSO READ: Your Guide to Become A Successful Personal Trainer
Long-term and Short-term Benefits of Calorie Dumping
Short-term benefits include replenishing glycogen stores, boosting metabolism, and providing mental relief from a strict diet.
Also known as a "refeed" or "cheat day," bodybuilders do calorie dumping for several long-term reasons:
Best Foods for Calorie Dumping
Bodybuilding
Chia Seeds in A Bodybuilder’s Diet: An Expert’s Advice

Chia seeds are a nutrient-dense food, offering protein, fiber, healthy fats, and various vitamins and minerals. While they're not a direct source of muscle-building protein like meat or eggs, they can complement a balanced diet by providing essential nutrients important for overall health, which indirectly supports muscle development when combined with a proper exercise routine. However, solely relying on chia seeds for building muscle mass might not be sufficient—you'd likely need a variety of protein sources along with a consistent workout regimen for optimal muscle growth.
Chia seeds are popular among bodybuilders due to their high protein and omega-3 fatty acid content. They provide a good source of nutrients, help in muscle repair, and offer sustained energy throughout workouts. Additionally, their high fiber content can aid in digestion and help manage hunger, which can be beneficial for those trying to maintain a specific diet while building muscle.
Where to Buy Chia Seeds for Your Bodybuilding Diet
These are commonly available in various grocery stores, health food stores, and even online marketplaces like Amazon or specialty health websites. You can check your local supermarkets, health food stores, or browse online to purchase chia seeds for your bodybuilding diet. Many health-focused stores offer bulk options, which can be more cost-effective if you plan to use them regularly in your diet.
You can also try purchasing the seeds from popular online retailers like Walmart, or health food stores such as Whole Foods Market, Thrive Market, or Vitacost. There are also specialty health stores like iHerb or The Vitamin Shoppe that carry chia seeds.
Related Article: A New Caffeine? What You Need to Know about Teacrine
Preparation
These magical seeds can be quite versatile in the kitchen! Here are a few methods you can try:
After cooking it, you can serve them in various ways. You might consider adding them to yogurt, smoothies, oatmeal, or salads for an added nutritional boost. You can also use them in baking as an egg substitute or make a chia pudding by mixing them with your choice of liquid (like almond milk) and allowing them to gel.
What A bodybuilder Gets From the Magical Seeds
Rich in Protein
Chia seeds are a great source of plant-based protein, containing roughly 4.7 grams of protein per ounce. For bodybuilders, their protein content is beneficial for muscle repair and growth.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
They are an excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). These healthy fats support heart health, reduce inflammation, and aid in muscle recovery, all beneficial for bodybuilders. The omega-3s in chia seeds can also help maintain joint health, enhance stamina, and assist in managing weight. Integrating chia seeds into a balanced diet can contribute to overall well-being and support a bodybuilder's goals.
Fiber Content
They contain a high amount of soluble and insoluble fiber, with about 10 grams of fiber in a 1-ounce (28-gram) serving.
Helps with digestion and promotes a feeling of fullness, aiding in weight management.
Antioxidants
The seeds contain antioxidants like flavonoids and phenolic compounds that help combat oxidative stress in the body, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases. These antioxidants can help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Including chia seeds in your diet can contribute to overall health and well-being due to their antioxidant properties. Fight off free radicals that can damage cells post-workout with these magical seeds.
Minerals
They contain calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, and manganese, contributing to bone health, energy metabolism, and antioxidant activity. These minerals support various bodily functions, from maintaining strong bones to aiding muscle function and energy production.
Hydration
When soaked, they form a gel that retains water, aiding in maintaining hydration during workouts.
What Are The Disadvantages of Overconsuming Chia Seeds
Chia seeds can be beneficial for bodybuilders due to their nutrient content, but overconsumption might cause gastrointestinal issues or interfere with hydration.
They're high in fiber, so eating too many could cause digestive problems like bloating or diarrhea. Plus, their omega-3 fatty acids might interact with certain medications or cause allergic reactions in some people. Moderation is key!
Overall
In summary, Chia seeds are a powerhouse for bodybuilders! They offer a high protein content, essential for muscle repair and growth. Additionally, they're packed with omega-3 fatty acids for reducing inflammation and providing sustained energy during workouts. Their fiber content aids in digestion and helps maintain a steady release of energy. Plus, their versatility allows for easy incorporation into shakes, smoothies, or as a topping for meals, making them a convenient addition to a bodybuilder's diet.
Don't Miss: 10-Week Army Combat Fitness Test (ACFT) Plan
Nutrition
Everything Nutritional Food: What’s Too Much Or Too Little

When it comes to bodybuilding, overeating can result in consuming too many calories and potentially gaining weight, which may not be ideal for muscle building. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a balanced and personalized nutrition plan that aligns with your specific goals. By that we're talking about nutritional food every bodybuilder must stick to.
Consuming more calories than your body needs for muscle growth can lead to fat gain. Similarly, not eating enough food can hinder muscle development. It's crucial to calculate your calorie and macronutrient needs based on your goals and activity level and consult with a fitness or nutrition professional for personalised guidance.
How to Measure Calories to Ensure Nutritional Food as a Bodybuilder
As a bodybuilder, accurately measuring calorie intake is crucial for your nutrition plan. Here are some steps to help you count calories in your food:
Use a Food Scale
Invest in a digital kitchen scale to weigh your food. This allows you to measure portions accurately.
Read Nutrition Labels
Many packaged foods have nutrition labels that provide calorie information per serving. Pay attention to serving sizes and servings per container.
Use Calorie Tracking Apps
Many smartphone apps like MyFitnessPal and Cronometer make it easy to track your calorie intake. You can search for the foods you're eating and specify the portion size, and the app will calculate the calories.
Reference Online Databases
If you can't find a nutrition label, you can often find calorie information for various foods in online databases and reference books.
Learn to Estimate
Over time, you'll better estimate portion sizes and calorie content. This skill is valuable when you can't weigh or measure every meal.
Consider Macronutrients
While tracking calories, don't forget to pay attention to your macronutrient intake (proteins, carbs, fats). These are also crucial for bodybuilders.
Be Consistent
It's essential to be consistent in tracking. Measure and record your food every day to get a better understanding of your calorie intake.
Adjust for Cooking
Remember that cooking can change food weight (due to water loss). Weigh food before cooking for more accurate calorie tracking.
Consult a Nutritionist
If you're unsure about your calorie needs or struggle with tracking, consider consulting a registered dietitian or nutritionist who can help you create a personalised nutrition plan.
Related Article: 30 Gym Slang Terms Explained
Measuring and tracking calories accurately is an essential part of bodybuilding, as it helps you control your intake and adjust your diet to meet your specific goals.
Nutritional Food You Must Include In Your Diet
To effectively build muscle mass, it's essential to maintain a balanced diet consisting of nutrient-rich foods. Here are some foods that are best for building muscle:
1. Lean Proteins
Protein is essential for muscle growth. Opt for lean sources like chicken, turkey, fish, lean beef, tofu, tempeh, eggs, and low-fat dairy products. Plant-based sources like beans, lentils, and quinoa are also excellent options.
2. Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates provide energy for workouts and recovery. Choose complex carbs like whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats), sweet potatoes, and whole-wheat pasta.
3. Healthy Fats
Good fats are essential for overall health. Include sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil.
4. Dairy or Dairy Alternatives
Dairy products and dairy alternatives like almond milk or soy milk can provide additional protein and calcium.
5. Fruits and Vegetables
These are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which support overall health and recovery.
6. Nuts and Seeds
Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are excellent sources of healthy fats and protein.
7. Greek Yogurt
It's high in protein and can be a good snack or breakfast option.
8. Salmon
Rich in omega-3 fatty acids and high-quality protein, salmon can support muscle growth and overall health.
9. Quinoa
A complete protein source and a great alternative to rice or pasta.
10. Beans and Lentils
These are excellent sources of plant-based protein and fibre.
11. Whey Protein
A convenient way to supplement your protein intake, especially post-workout.
12. Eggs
Eggs are a highly bioavailable source of protein and contain essential amino acids.
13. Lean Beef
It provides high-quality protein, iron, and essential nutrients.
14. Chicken or Turkey Breast
Lean poultry is a staple for many bodybuilders due to its protein content and low-fat
15. Tofu and Tempeh
Good plant-based protein sources, especially for vegetarians and vegans.
16. Cottage Cheese
It's high in protein and low in fat, making it a great addition to your diet.
A well-balanced diet is vital. Ensure you consume enough calories to support muscle growth and consider your macronutrient balance. Staying hydrated is also essential. You might need to adjust your calorie and protein intake based on your goals, activity level, and body size, so it's a good idea to consult a nutritionist or dietitian for a personalised plan.
Should Bodybuilders Avoid Some Not-So- Nutritional Food Altogether?
While there are no foods that bodybuilders must avoid, some foods are less ideal due to their potential negative impact on health and fitness goals. These include:
Read More: Meet the World’s Strongest Grannies
Processed Foods
Highly processed foods are often high in empty calories, added sugars, unhealthy fats, and low in nutrients. They can contribute to weight gain and hinder muscle-building efforts.
Sugary Snacks and Beverages
Foods and drinks with excessive added sugars can lead to energy spikes and crashes, as well as weight gain. They offer little nutritional value.
Trans Fats
Foods containing trans fats, such as many fast-food items and some packaged baked goods, are linked to heart disease and should be limited
Sugary Cereals
Many breakfast cereals contain added sugars and lack essential nutrients. Opt for whole-grain, low-sugar options instead.
Alcohol
Excessive alcohol consumption can impair muscle recovery and protein synthesis. It can also contribute to dehydration and poor dietary choices.
Excessive Fast Food
While an occasional indulgence is acceptable, relying on fast food for a significant portion of your diet can lead to poor nutrition and hinder muscle gains.
Highly Caffeinated or Sugary Energy Drinks
These may provide a temporary energy boost, but the sugar and caffeine content can harm health and lead to crashes.
Fried Foods
Fried foods often contain unhealthy fats and calories. While occasional consumption is acceptable, they shouldn't be a regular part of your diet.
Excessive Saturated Fats
Limit foods high in saturated fats, like fatty cuts of red meat and full-fat dairy products. While some saturated fats are okay, too much can harm heart health.
Excessive Salt
High-sodium foods can lead to water retention and may negatively affect blood pressure. Limit processed foods and opt for fresh, whole foods.
It's essential to maintain balance and moderation in your diet. Occasional indulgences are OK, but your primary focus should be on nutrient-dense, whole foods that support your muscle-building and overall health goals. Consulting with a nutritionist or dietitian can help you create a personalised diet plan that aligns with your objectives.
Sea Food to Consider for Gains
Seafood is a healthy and delicious choice, rich in protein, omega-3 fatty acids, and various essential nutrients. Here are some healthy seafood options and basic preparation methods:
Salmon:
-
- Grilled: Season with herbs, spices, and a bit of olive oil, then grill until it flakes easily.
- Baked: Marinate with lemon, herbs, and olive oil, then bake in the oven.
- Pan-Seared: Sear in a hot skillet with a little oil, skin side down, until crispy, then finish in the oven.
-
Tuna:
- Sushi/Sashimi: Serve raw as sashimi or in sushi rolls.
- Grilled or Broiled: Season with soy sauce, ginger, and garlic, then grill or broil until desired doneness.
-
Shrimp:
- Shrimp Scampi: Sauté in garlic, butter, and white wine.
- Grilled: Thread onto skewers and grill with marinade or spices.
-
Cod:
- Baked: Coat with breadcrumbs and herbs, then bake until it flakes easily.
- Poached: Simmer in seasoned broth or white wine until opaque.
-
Mackerel:
- Pan-Fried: Coat with a light breading, then pan-fry until crispy.
- Smoked: Serve smoked mackerel with crackers and cream cheese.
-
Sardines:
- Canned: Eat canned sardines with olive oil, lemon, and crackers or on top of a salad.
- Grilled: Season and grill sardines with olive oil until they're crisp and fragrant.
-
Trout:
- Stuffed: Stuff with herbs, lemon, and garlic, then bake or grill.
- Almondine: Sauté with butter, lemon juice, and toasted almonds.
-
Haddock:
- Baked: Season with herbs and breadcrumbs, then bake until tender.
- Poached: Poach in a flavorful broth or white wine.
-
Scallops:
- Pan-Seared: Sear in a hot pan with butter or oil for a few minutes on each side.
- Broiled: Season and broil until lightly browned and opaque.
When preparing seafood, remember to handle it safely and avoid overcooking, as seafood tends to become dry when overdone. You can customize these cooking methods with various herbs, spices, and sauces to suit your taste preferences. Additionally, be mindful of sustainable seafood choices and check for local advisories on fish consumption, especially for pregnant women and children, due to potential mercury content.
Must Read: Using SARMs on Top of a Steroid Cycle: DOs and DON
Proper Storage of Food to Keep It Fresh
-
Refrigeration:
- Keep perishable items like meat, dairy, and leftovers in the refrigerator at or below 40°F (4°C).
- Store raw meat separately to prevent cross-contamination.
- Use airtight containers or food storage bags to seal items to prevent moisture loss and odors from spreading.
-
Freezing:
- Freeze items at 0°F (-18°C) or lower for long-term storage.
- Use freezer-safe containers or vacuum-sealed bags to prevent freezer burn.
- Label items with the date to keep track of storage time.
-
Pantry:
- Store dry goods like pasta, rice, and canned foods in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Use airtight containers to keep pests out and maintain freshness.
-
Fruits and Vegetables:
- Some fruits and vegetables should be stored separately due to ethylene gas production (e.g., apples and avocados).
- Check for specific requirements for each item, as some should be stored in the fridge, while others are better at room temperature.
-
Keep an Eye on Expiration Dates:
- Regularly check expiration dates on packaged foods and discard items that have passed their date.
-
Properly Seal Containers:
- Ensure containers are tightly sealed to prevent moisture and air from entering, which can lead to spoilage.
-
FIFO (First In, First Out):
- Practice the "first in, first out" method to use older items before newer ones to avoid food waste.
-
Handle Leftovers:
- Refrigerate or freeze leftovers promptly, and use them within a reasonable time frame.
-
Be Mindful of Temperature Zones:
- Know the temperature zones in your fridge (e.g., coldest at the back and warmest on the door) and store items accordingly.
-
Regularly Clean Your Storage Areas:
- Clean your refrigerator, pantry, and cabinets to prevent the growth of bacteria and mold.
Remember that specific foods may have unique storage requirements, so it's important to check packaging labels and do some research when in doubt. Proper food storage helps maintain freshness and reduces food waste.
Packing Your Food Discretely to Eat at the Gym
- Choose the right container: Opt for containers that are compact and easy to carry, like a small Tupperware or a bento box.
- Select inconspicuous foods: Choose foods that are quiet to eat and won't disturb others. Avoid noisy snacks like chips.
- Pack pre-portioned snacks: Prepare single servings of your snacks to avoid rustling around in a noisy bag or container.
- Use noise-reducing wrappers: Wrap your snacks in noise-dampening materials, like cloth napkins or silicone food wraps, to reduce crinkling sounds.
- Opt for quieter options: Consider snacks like protein bars, pre-cut fruit, or a smoothie in a shaker bottle, which are less likely to make noise.
- Be mindful of odors: Choose foods that won't emit strong odors in the gym. Stick to odorless options like nuts, dried fruit, or yogurt.
- Pack a reusable water bottle: Bring a reusable, non-disruptive water bottle to stay hydrated without making noise with plastic crinkling.
Remember to be respectful of others in the gym and maintain good hygiene when consuming your discreetly packed food.
Going for a Jog and Want to Snack In Between?
Snacking while jogging can be tricky, as it's important to maintain focus on your run and safety. If you need a quick energy boost, consider portable, easy-to-eat options like energy gels or chews that can be consumed with minimal interruption.
Just make sure to dispose of the packaging responsibly. Hydration is often more critical than snacking during a run, so prioritize water or a sports drink for longer workout.
It's best to consume easily digestible snacks that provide a quick energy boost. Some good options include energy gels, granola bars, banana slices, or a handful of raisins.
When running or jogging, it's important to consume snacks that provide a quick energy boost and are easy to carry. Some good options include:
- Energy gels or chews: These are specifically designed for quick energy replenishment during exercise.
- Bananas: They're portable, rich in carbohydrates, and contain potassium.
- Trail mix: A mix of nuts, seeds, and dried fruits can provide a good balance of nutrients.
- Nut butter packets: Portable and packed with healthy fats and protein.
- Rice cakes or rice bars: A lightweight, easy-to-carry option with carbohydrates.
- Fig bars: These provide a blend of carbohydrates and are easy to eat on the go.
You can always experiment to find what works best for your body and your preferences while running.
Tips to Prepare a healthy Balanced Nutritional Food
Preparing a healthy, balanced meal as a bodybuilder involves selecting the right components in the proper proportions. Here are steps to help you prepare such a meal:
1. Choose a Lean Protein Source
Start with a lean protein source such as chicken, turkey, fish, lean beef, tofu, or beans. Protein is crucial for muscle growth and repair.
2. Add Complex Carbohydrates
Incorporate complex carbohydrates like brown rice, quinoa, sweet potatoes, or whole-wheat pasta. Carbs provide energy for your workouts and help replenish glycogen stores.
3. Include Vegetables
Vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fibre. Opt for various colourful options, like broccoli, spinach, bell peppers, and carrots.
4. Incorporate Healthy Fats
Include sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, or olive oil. Fats are essential for overall health and hormone production.
5. Measure Portions
Use a food scale to measure and control your portion sizes. Balancing your macros (protein, carbs, and fats) is essential.
6. Season and Flavor
Use herbs, spices, and low-sodium sauces to add flavour to your meal without excess calories or sodium.
7. Hydrate
Don't forget to drink water. Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and muscle function.
8. Preparation Methods for Nutritional Food
Opt for healthy cooking methods like grilling, baking, steaming, or sautéing with minimal oil. Avoid deep-frying.
9. Post-Workout Nutrition
After a workout, consider a post-workout meal or shake that combines protein and carbohydrates to support muscle recovery and replenish glycogen stores.
10. Plan
Meal planning and preparation in advance can help you stick to your nutrition goals. Cook larger batches and store leftovers for future meals.
11. Monitor Progress
Keep track of your dietary intake and how it affects your body and performance. Adjust your meal plan as needed to meet your goals.
12. Consult a Nutritionist
If you're unsure about portion sizes, macros, or specific dietary needs, consult a nutritionist or dietitian who can create a customised nutrition plan.
It's important to customize your meals to your individual goals, activity level, and dietary preferences as everyone's nutritional needs vary. Consistency in healthy eating, combined with a well-structured workout plan, will contribute to success in bodybuilding.
Best Calorie-Measuring Equipment and Machines
For bodybuilders and fitness enthusiasts looking to accurately measure calorie intake, various kitchen appliances and gadgets can be helpful. Here are some of the best calorie-measuring machines and tools:
Digital Kitchen Scale
A high-quality digital kitchen scale is essential for measuring the weight of food items accurately. It allows you to calculate calories based on portion size.
Nutrition Scale
Some kitchen scales have built-in nutritional information databases. You can input the food item's code or name, and the scale calculates the nutritional content, including calories.
Smartphone Apps
There are several smartphone apps, such as MyFitnessPal and Cronometer, that allow you to track your calorie intake by searching for foods and specifying portion sizes. These apps often have extensive food databases.
Food Processors with Nutrition Calculators
Some food processors have built-in nutrition calculators that provide information about the calories, macronutrients, and other nutritional content of your recipes.
Smart Kitchen Gadgets
Various smart appliances, like intelligent blenders and air fryers, may have built-in nutrition tracking features. They can provide approximate nutritional information for your recipes.
Handheld Calorie Counters
These portable devices are designed precisely to calculate the nutritional content of food. You input the food item or scan its barcode, and the device provides calorie information.
Online Recipe Analyzers
There are websites and software tools that allow you to input the ingredients and quantities of your recipes, and they will calculate the nutritional content, including calories.
Meal Prep Containers
While not a machine per se, having portion-controlled meal prep containers can help you estimate and control calorie intake by pre-measuring your meals.
When it comes to measuring calories, choosing the right tool depends on your preferences and requirements. Digital kitchen scales are essential for precise portion control, while smartphone apps offer convenience and access to extensive databases. Consider your budget, the features you need, and your level of tech-savviness before selecting the appropriate calorie-measuring machine to help you achieve your bodybuilding goals.
Why Bodybuilders Must Eat Healthy Before a Competition
Bodybuilders must eat healthy before a competition for several important reasons:
1. Optimal Performance
Eating a nutritious diet before a competition ensures your body is fueled and ready to perform at its best. Nutrient-dense foods provide the energy required for intense workouts and help maintain strength and stamina during the competition.
2. Muscle Preservation
Proper nutrition helps preserve lean muscle mass. In the weeks leading up to competition, bodybuilders often go through a cutting phase to reduce body fat. Eating a balanced diet with adequate protein helps prevent muscle loss while shedding excess fat.
3. Nutrient Timing
The timing of meals and nutrient intake is crucial. Bodybuilders typically follow a precise nutrition plan leading up to competition, including carb-loading to maximise muscle glycogen stores and protein intake to support muscle repair and growth.
4. Recovery
Nutritional food aids in recovery between workouts. Intense training sessions can lead to muscle damage, and consuming the proper nutrients helps speed recovery and reduce the risk of overtraining.
5. Aesthetics
The appearance of bodybuilders on stage is highly dependent on their diet. The right balance of macronutrients, proper hydration, and avoiding foods that cause bloating or water retention contribute to a more chiselled and defined physique.
6. Mental Focus
Nutrition affects mental clarity and focus. Eating a healthy diet before a competition can help bodybuilders stay mentally sharp, making it easier to follow their routines and perform their best.
7. Digestive Comfort
Avoiding foods that can cause digestive discomfort, such as excessive fibre or spicy foods, is crucial to prevent gastrointestinal issues during the competition.
8. Hydration
Proper hydration is vital for overall health and performance. Dehydration can lead to muscle cramps, fatigue, and decreased athletic performance.
9. Body Composition
Following a clean, balanced diet helps bodybuilders reach their target body composition with minimal fat and maximum muscle definition, which is essential for success on stage.
Conclusion
To sum up, maintaining a healthy diet is extremely important for various reasons such as enhancing physical performance, preserving muscles, quick recovery, improving appearance, increasing mental focus and achieving overall success. Bodybuilders meticulously plan their diets not only to ensure they are in top condition for competition day but also to maintain optimal physical fitness.
Also Read: Running and Bodybuilding: Is it a Good Idea to Mix Them?
-

 Bodybuilding2 years ago
Bodybuilding2 years agoNew Arrival Workout Equipment on Amazon for The Disabled
-

 Steroids2 years ago
Steroids2 years agoSupplemental Breast Milk for Bodybuilders: The Secret Behind It
-

 Steroids2 years ago
Steroids2 years agoDwarf Bodybuilders Giving Pros A Run for Their Money
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoVOX Testing: Why Bodybuilders Must Have It Tested Regularly
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoShavers and Other Body Grooming Equipment for Bodybuilders In 2023
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoChatGPT and Other Avenues to Find Great Bodybuilding Coaches
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoBest Oil Recommendations Before Competition for Subtle Shimmer
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoPowerlifting Vs Power Building: Find Out the Big Difference and When to Shift Between the Two
-

 Beginners12 months ago
Beginners12 months agoTren Cycle for Beginners
-

 Bodybuilding11 months ago
Bodybuilding11 months agoCompetition Prep Cycle for Pro Bodybuilders
-

 Nutrition9 months ago
Nutrition9 months agoEverything Nutritional Food: What’s Too Much Or Too Little
-

 Anabolic Steroids8 months ago
Anabolic Steroids8 months agoLegality of Anabolic Steroids In Latin America
-

 Bodybuilding8 months ago
Bodybuilding8 months agoChia Seeds in A Bodybuilder’s Diet: An Expert’s Advice
-
 Bodybuilding6 months ago
Bodybuilding6 months agoList of FDA-Approved Peptides
-

 Anabolic Steroids9 months ago
Anabolic Steroids9 months agoNatural Steroids for Bodybuilding
-

 Anabolic Steroids7 months ago
Anabolic Steroids7 months agoStart The New Year Strong With These Tips
-

 Beginners9 months ago
Beginners9 months agoCalisthenics: Secret to Building A Better Upper and Middle Body
-

 Bodybuilding7 months ago
Bodybuilding7 months agoUnique Things That Have Redefined Mr Olympia Over The Years
-

 Steroids5 months ago
Steroids5 months agoTrenbolone: Why it Remains A Beast In the Market
-

 Bodybuilding Products4 months ago
Bodybuilding Products4 months agoTelmisartan In Bodybuilding: An Expert’s Advice
-
 Bodybuilding5 months ago
Bodybuilding5 months agoThe Importance of Scaptions in Female Athletes
-

 Bodybuilding4 months ago
Bodybuilding4 months agoHow Much Is Too Much Cardio? Understanding Heart Rate Zones
-

 Bodybuilding6 months ago
Bodybuilding6 months agoFunny Gym Stories and Moments to Light Up Your Day
-

 Steroids8 months ago
Steroids8 months agoThese Bodybuilding Equipment Might Become Obsolete Next Year (See Alternative Upgrades)
-

 Bodybuilding7 months ago
Bodybuilding7 months agoCalorie Dumping: A Bodybuilder’s Guide