Supplements
Bodybuilding Protein Cycling for Massive Gains

Mistakes, Protocol, Pros and Cons
There is no bodybuilding without protein. Protein cycling(PC) is a strategy where bodybuilders alternate between high, low, and average protein consumption. A high-protein diet is a secret to hardcore bodybuilding, but it will not help you maintain the perfect body; protein cycling does. Your body needs various kinds of proteins to grow and strengthen muscle naturally and from supplements. Protein cycling is based on measured protein consumption from considerable amounts of protein and different sources, generally within a two-week cycle.
However, high protein consumption, for a long time, has been found to induce anabolic resistance. Athletes such as bodybuilders must pay attention to how their body rehydrates, replenishes, and repairs after every exercise. That will help you adapt to training faster than usual and reduces the chances of getting fatigued. Additionally, skeletal muscles normally mass with aging.
Related Article:: Protein Powder Supplement Comparison – Which Type To Choose?
Anabolic resistance refers to reduced muscle ability to stimulate protein synthesis. Aging comes with anabolic resistance even though feeding-induced simulation remains constant. However, some elements of feeding resistance affect their protein intake significantly for some people.
Helpful Facts in Protein Cycling
You should take one gram of protein per pound of body weight. Every fitness enthusiast must follow this religiously if they want to have an enviable body. Most fitness professionals have achieved a lot body-wise by ensuring their body is not short of proteins needed for MPS. Additionally, they can take only what will contribute to muscle growth without necessarily adding extra pounds of fat. If you weigh 250 pounds, you must take anywhere between 240 and 260 grams of protein daily.
Although this might be difficult to achieve due to many factors, it is important to ensure it is done four days a week. Otherwise, you might not complete the required muscle mass. Moreover, your exercise rate and intensity will dictate whether you need slightly more or less of the recommended amount. Elite bodybuilders, for example, can take up to 2 grams per pound of their body weight. If a bodybuilder wants to increase protein synthesis and nitrogen retention, they must take high-protein foods like beef, fish, chicken, etc.
Muscle Growth
Rapid muscle growth does not only stop at taking more protein. It involves taking them correctly and with carbs. Additionally, the diet must also include proper fat intake. The trick is to balance the three, not substituting one with the other. As mentioned earlier, taking too much or too little protein might not achieve the desired results as far as bodybuilding and fitness are concerned. It doesn’t matter whether your body is natural; only take the protein it can accommodate.
Also, people are wrong to assume that carbs are entirely bad and proteins are reasonable. As long as the balance is maintained, then you’re good to go. Fats, on the other hand, are a bit different. The fact about fats is that you will get fat if you take more fat, but the reverse is invalid. Depending on your routine, only take a certain amount of fat daily. For instance, you cannot take the same amount of fat when doing intensive exercises and light ones like just training your shoulders. You will need more energy to do deadlifts and other full-body routines; most of that energy comes from burning fat.
Protein Cycling Protocol
Excess fasting and protein cycling are undoubtedly the best way to slow down aging for bodybuilders. Additionally, there is growing evidence that protein cycling helps prevent cancer, heart disease, and diabetes. While the average human takes about 70 grams of protein daily, bodybuilders need about twice to maintain muscle mass. A typical bodybuilder protein cycling involves halving protein intake within the first five days and doubling it afterward. Depriving your body of proteins within the first five days enhances autophagy, which is your body's process of carrying out protein recycling.
Today's greatest bodybuilders have successfully stimulated more excellent protein retention through protein cycling. And that is precisely where the secret to their success lies. Unknown to many, protein cycling is not something easy to go about. The truth is that many people struggle to make this dream a reality, something that has dramatically affected their fitness careers. For bodybuilding newbies, we will show you the steps you can use for proper protein cycling.
Step 1: Reduce Protein Intake for the First 5 Days
For about five days, reduce the amount of protein you take considerably to maybe half the amount you used to take. However, it is recommended that you take not more than 1 gram of protein per 1 pound of body weight within those five days and see how your body responds to the change. It would help if you weren’t worried that you might shrink within those few days. No, it takes much longer for your muscle mass to show a significant reduction. However, be careful not to take too little protein during that period. You must not go below 0.5 grams per pound of body weight.
Although your body may change its metabolic rate to accommodate protein deficiency, there is a specific limit on how much change it can sustain. The resulting anti-catabolic effect from reduced protein metabolism has been found to enhance muscle growth. Regularly decreasing your protein intake induces muscle preservation in your body. At the same time, your muscles will be growing at almost the same rate as before. The result is increased muscle mass over a relatively short period.
Step 2: Increase Protein Intake After 5 Days
Up your protein intake after the first five days. Remember that the first step involved reducing protein consumption to induce enzymatic anti-catabolism. Once you switch gears in this second stage and start taking more protein, your body accumulates more protein and builds muscle. The enzymes that cause protein anti-catabolism will slow metabolism, while the protein consumption surge will enhance muscle growth. Bodybuilders with more than 200 pounds should start taking between 1.5 and 1.8 grams of protein per pound at this stage. You should increase the rate to 2 grams per pound daily for ten days if you’re on a two-week cycle. All this is geared towards helping the body achieve a hyper-anabolic state, highly enzymatic and ideal for muscle growth.
Must Read:: Best Diet Plan for Bodybuilders 2019
Protein Cycling Mistakes to Avoid
Protein cycling may not achieve your desired results if you don’t do some things right. Here are some protein cycling mistakes to avoid.
1. Taking More Than You Can Sustain
Some bodybuilders are impatient and want instant transformation. While bodybuilding is about gratification, be careful not to overwhelm your body with proteins. Most protein foods promise quick results with certain restrictions in terms of what amount to take and how to take it. It is very tempting to bypass such requirements and do everything you like. That is disadvantageous from many angles. One is that you may take in extra calories, which may not help you achieve the ideal muscle mass.
Gold Standard >> Buy It <<
Similarly, taking protein foods with meager calories and too many of them may experience painful weight loss. You are not supposed to lose more than the recommended weight as a bodybuilder because it might take longer to recover. Most people will generally gain their weight back after six months. That is a bit too long in professional bodybuilding and fitness. It would be best never to take in more protein than your body can sustain.
2. Changing Programs Frequently
You can only engage in beneficial protein cycling if you stick to one working program. Unfortunately, many bodybuilders may hop from one program to another, which is not advisable. The reason is that you may erase the gains you have made in the previous cycling program when you shift to a new one. Additionally, you may not get any results if you are not patient enough to finish the program. There is no other secret to getting results in protein cycling except patience and consistency with the chosen program. Even when losing confidence and motivation, stick to your schedule anyway. You will be surprised at how fast you will get the desired results when you stick to one plan. Note that changing programs involves reducing the amount of protein to take in grams per pound of body weight.
3. Setting Unrealistic Goals
Aiming high but not having expectations that exceed your abilities is okay. You may never achieve anything if you form a habit of coming up with unrealistic bodybuilding goals regarding protein cycling. If you want to increase muscle significantly within a short time, you may be forced to consume more proteins than recommended. You may not only fail to achieve your ‘goal’ but also jeopardize your entire bodybuilding career. Weight loss and muscle gain take time, and setting your expectations too high will only bring frustration. The reason is that you will always feel like you are not getting what you deserve, even though you put a lot of effort into it.
4. Losing Focus as Soon as You Begin a Nutrition Program
Protein cycling to lose a certain amount of fat or attain a particular lean muscle mass is no walk in the park. You have to drive yourself every day with unwavering discipline. That kind of consistency will give you the results you need. You may not achieve the results 100%, but you will get up to 90% with character. Whether you will maintain your focus to the end of the program depends on the nutrition program you choose. For this reason, it is essential that you only go for a sustainable program, as indicated in No. 1 above.
Related Article:: Top 10 best Immune Boosting Supplements to buy in 2020
Protein Cycling Pros and Cons
Protein cycling bodybuilding is not without immense benefits as well as drawbacks. While you may not realize all the advantages you need, you are assured that more than 50% gains, at least mentioned, don’t make your expectations so high because this process takes time. The following are some pros and cons associated with protein cycling.
Pro: Most protein foods are easy to find
Most bodybuilders have tight schedules and do not get the time to get protein foods not found in their locality. Luckily, most protein isolates are pretty accessible and convenient. Take the case of a milkshake, for example; it is virtually at arm’s length in your nearest store.
Con: Protein powder doesn’t contain all the nutrients you may need
Even if you get a convenient protein supplement, you may still be forced to look for other food nutrients not found in it. That cancels the convenience of finding something like a protein powder shake somehow.
Pro: Older bodybuilders benefit the most from protein cycling
It has been established that older bodybuilders benefit the most from protein cycling due to their bodies’ enhanced protein sustainability. Most of them engage in highly intensive training exercises that enable them to take between 1.6 to 2 grams per pound of body weight and get more results. On the other hand, young bodybuilders can only take 0.5 to 1.2 grams of proteins per pound to get the desired results. It is doubtful that young bodybuilders will get any additional benefits from taking more than 1.8 grams per pound.
Con: You don’t need only supplements for protein cycling
You can attain the recommended protein intake by taking ordinary high-protein foods such as fish, eggs, beef, Almonds, lentils, soy milk, and many more. That means you don’t necessarily have to take protein supplements to achieve lean muscle mass or weight loss.
Pro: Protein Powder is the perfect supplement for weight loss
As you may already know, protein powder is a highly concentrated protein source for bodybuilders looking to lose weight. Pro bodybuilding requires constant muscle mass, and taking protein powder in their cycles ensures they do not accumulate many calories at the expense of muscle.
Con: You will come across protein supplements with too much sugar and other additives
Without sugars and other additives, you may not stand the taste of most protein isolates. Although these substances improve the taste and make the supplements worth eating, they are unsuitable for bodybuilders. Unless you are ready to put up with the awful taste of protein supplements left on your mouth, supplements, sugars, and other additives will always be a part of your protein cycling diet.
Protein Cycling Side Effects
Protein cycling is a relatively new concept, and little research has been conducted. The process has been found to have specific side effects on bodybuilders. However, it is essential to note that side effects happen in every aspect of bodybuilding. It is somehow normal, so you shouldn’t freak out about experiencing some of them unless they become life-threatening. Here are some common side effects associated with protein cycling:
- Thirst
- Possible kidney damage and malfunction
- Loss of appetite
- Loss of muscle
- Nausea
- Increased bowel movements and cramps
- Interference of the body’s nutrient absorption
List of Amazon Products for Protein Cycling
Medline ENT693SFOC Active Liquid Protein
Medline ENT693SFOC Active Liquid Protein
BioTrust Low Carb Protein Powder
BioTrust Low Carb Protein Powder
Thinner Leaner Stronger
Conclusion
As stated in this Article's first sentence, protein is king in bodybuilding and is the main dietary factor for every athlete. However, it is how you take it that makes the difference. Protein cycling becomes a viable option when you feel like your body is no longer retaining as much protein as necessary for your bodybuilding purposes. Let no one lie that protein cycling only works for a particular group. Every bodybuilder can benefit from protein cycling if they follow the proper protocol.
Bodybuilders work longer and harder than most athletes, so they need the means. The means here means more significant muscles to sustain the intensive workouts. The bodybuilder can maintain good form throughout the season with protein cycling. Pro bodybuilders no longer follow the tradition of taking one gram per pound of their body weight. The reason is that the industry is increasingly becoming more competitive, and only the best make it to the top.
Overall
Protein cycling has enabled them to beat opponents to the title by eating as much as 2.5 grams per pound of protein. However, there is always a limit on how much protein a bodybuilder should consume. The limit depends on how much protein your body can sustain to help you reach your full potential. That means you must study your body to determine your protein intake limits.
Product Reviews
Top Vitamins for Skin Health
Bodybuilders have unique nutritional needs due to their intense training regimens.
Here are compelling reasons why bodybuilders (and anyone, really) should pay attention to their vitamin intake for healthy skin:
Related Article: Are the Fruits Helpful For Body Fat Loss?
Cell Repair and Regeneration
Vitamins play a crucial role in cell repair and regeneration. Skin cells constantly undergo wear and tear due to exercise, sun exposure, and other factors. Adequate vitamins support the renewal process, helping maintain healthy skin.
Collagen Production
Collagen is a protein that provides structure and elasticity to the skin. Vitamins like vitamin C and vitamin E are essential for collagen synthesis. Without enough collagen, skin can become saggy and lose its youthful appearance.
Antioxidant Defense
Vitamins such as vitamin A, vitamin C, and vitamin E act as powerful antioxidants. They protect skin cells from damage caused by free radicals, which can accelerate aging and contribute to wrinkles and fine lines.
Wound Healing
Bodybuilders often experience minor cuts, bruises, or skin abrasions during training. Vitamins like vitamin K and vitamin C are involved in wound healing and tissue repair. Ensuring sufficient intake aids in faster recovery.
Sun Protection
While sunscreen is crucial, certain vitamins provide additional natural sun protection. For instance, vitamin D (produced when skin is exposed to sunlight) supports overall skin health and may help prevent skin cancer.
Reducing Inflammation
Intense workouts can lead to inflammation. Vitamins like vitamin E and vitamin D have anti-inflammatory properties, helping soothe irritated skin.
Hydration and Moisture
Proper hydration is essential for skin health. Vitamins like vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid) help maintain skin moisture levels, preventing dryness and flakiness.
Skin Barrier Function
Vitamins B3 (niacin) and B7 (biotin) contribute to a healthy skin barrier. A strong barrier protects against environmental stressors and prevents water loss.
Reducing Acne and Blemishes
Some vitamins, like vitamin A, regulate sebum production and prevent clogged pores. This can help reduce acne and blemishes.
 Buy Penester (finasteride ) 5MG 28TAB
Buy Penester (finasteride ) 5MG 28TAB
Overall Health
Remember that skin health is closely linked to overall health. Vitamins support not only skin but also immune function, energy production, and muscle repair.
Generally, vitamins are essential for maintaining healthy, radiant skin. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains provides the necessary nutrients. If you have specific concerns, consult a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.
The Most Appropriate Vitamins for Bodybuilders
Let’s dive deeper into the world of vitamins and nutrients that can benefit your skin health. Here’s a list of 20 vitamins and supplements that can promote healthy skin:
Vitamin D
Known for bone health, vitamin D may also play a role in skin cancer protection. Adequate levels of vitamin D are associated with a lower risk of melanoma.
Vitamin C
An antioxidant that protects against free radical damage, vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis and overall skin health. Include citrus fruits, bell peppers, and strawberries in your diet.
Vitamin E
Another antioxidant, vitamin E helps protect the skin from oxidative stress and supports skin elasticity. Sources include nuts, seeds, and spinach.
Biotin
A water-soluble vitamin, biotin supports healthy skin, hair, and nails. You can find it in eggs and legumes.
Vitamin A
Essential for skin health, vitamin A promotes skin repair and maintains a healthy complexion. Leafy greens and carrots are good sources.
Multivitamins
Taking a multivitamin can ensure you get a balanced mix of essential nutrients, including those beneficial for skin health.
Vitamin K
Supports blood clotting and may help reduce dark circles under the eyes. Leafy greens and broccoli are rich in vitamin K.
Vitamin B3 (Niacin)
Helps maintain skin barrier function and reduces redness. Found in meat, fish, and whole grains.
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Supports skin hydration and wound healing. Avocado, mushrooms, and sunflower seeds are good sources.
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine)
Important for skin health and metabolism. Found in poultry, fish, and bananas.
Vitamin B7 (Biotin)
Essential for healthy skin, hair, and nails. Eggs, nuts, and sweet potatoes provide biotin.
Vitamin B9 (Folate)
Supports cell division and tissue growth. Leafy greens, legumes, and citrus fruits contain folate.
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin)
Helps prevent skin dryness and promotes overall health. Found in animal products like meat and dairy.
Selenium
An antioxidant that protects skin cells. Brazil nuts, seafood, and whole grains provide selenium.
Iron
Necessary for oxygen transport and skin health. Include lean meats, beans, and fortified cereals.
Copper
Supports collagen production and skin elasticity. Nuts, seeds, and shellfish contain copper.
Silica
Important for connective tissue and skin health. Whole grains, leafy greens, and oats are sources.
Collagen Supplements
While not a vitamin, collagen supplements can improve skin elasticity and hydration.
Remember that a well-balanced diet, along with proper hydration, is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. If you have specific concerns, consider consulting a dermatologist or a registered dietitian for personalized advice.
Non-Vitamin Supplements for Skin Health
While vitamins play a crucial role, there are also natural supplements that can benefit your skin. Let’s explore some options:
Hyaluronic Acid (HA)
Although not a vitamin, HA is a powerful compound for skin health. It helps retain moisture, promotes collagen production, and supports skin elasticity. You can find HA supplements or consider foods rich in it, such as bone broth and certain vegetables.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
These healthy fats are found in fatty fish (like salmon, sardines, and tuna) and flaxseeds. Omega-3s help reduce inflammation, which can positively impact skin health.
Zinc
Essential for skin repair and wound healing, zinc is found in legumes (such as lentils and chickpeas) and eggs. It also supports collagen synthesis, which contributes to skin strength and elasticity.
Collagen Peptides
This is a protein that makes up a significant portion of our skin. Collagen supplements (often in the form of peptides) may help improve skin elasticity and hydration.
Don't Miss: Top 15 Bulking Supplements Today
More Ways to Take Care of Your Skin
To maintain healthy skin, bodybuilders should consider a comprehensive approach that includes the following steps other than the use of vitamins.
Hydration
Internal Hydration: Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health and skin hydration. Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day.
External Hydration: Use moisturizers that are appropriate for your skin type to prevent dryness and flakiness. Look for non-comedogenic products to avoid clogging pores.
Hygiene
Showering Regularly: Shower immediately after workouts to remove sweat, bacteria, and dirt that can clog pores and cause acne. Use a gentle cleanser to avoid stripping the skin of natural oils.
Proper Cleansing: Use a mild, non-irritating cleanser twice a day. This helps to remove sweat and oils without damaging the skin barrier.
Diet and Nutrition
Balanced Diet: Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Vitamins and minerals such as Vitamin C, Vitamin E, and zinc are crucial for skin health.
Supplements: Consider supplements that promote skin health, such as omega-3 fatty acids, which can help with inflammation and skin elasticity.
Sun Protection
Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher sunscreen daily, especially if training outdoors. This prevents UV damage and reduces the risk of skin cancer.
Protective Clothing: Wear protective clothing, hats, and sunglasses to shield the skin from the sun.
Managing Skin Conditions
Acne: Use non-comedogenic products and consider over-the-counter treatments with benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid. For severe acne, consult a dermatologist.
Rashes and Irritation: Wear moisture-wicking, breathable fabrics to reduce friction and irritation. Apply anti-chafing products to areas prone to friction.
Rest and Recovery
- Adequate Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night. Sleep is crucial for skin repair and overall recovery.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. High stress levels can lead to skin issues like acne and eczema.
Regular Exfoliation
Gentle Exfoliation: Exfoliate 1-2 times a week with a gentle scrub or chemical exfoliant to remove dead skin cells and promote cell turnover. Avoid harsh scrubs that can cause micro-tears in the skin.
Avoiding Harmful Practices
Avoid Over-Washing: Over-washing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation.
Avoiding Steroid Abuse: Steroids can cause a range of skin issues, including acne, stretch marks, and thinning of the skin. If using performance-enhancing substances, do so under medical supervision.
Consulting Professionals
Dermatologist Visits: Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can help address any skin issues promptly and provide personalized skin care advice.
Personal Trainers and Nutritionists: Work with professionals to ensure that your training and diet support not just muscle growth, but overall health, including skin health.
Overall
By integrating these practices into their routine, bodybuilders can maintain healthy, vibrant skin that complements their physical fitness achievements.
Must Read: Human Chorionic Gonadotropin – A Hormone of Health
Bodybuilding
List of FDA-Approved Peptides
When it comes to bodybuilding, peptides have gained significant attention for their potential benefits in muscle growth and performance enhancement. However, it is crucial to prioritize safety and legality in the pursuit of achieving desired results.
Related Article: Best Post Cycle Therapy (PCT): 100% Recovery Within 6 Weeks
Why Peptides?
Bodybuilders use peptides for various reasons, including:
Muscle Growth
Some peptides, like growth hormone-releasing peptides (GHRPs) and growth hormone secretagogues (GHSs), are believed to stimulate muscle growth and repair, which can aid in muscle building.
Fat Loss
Certain peptides, such as melanotan II and peptide YY, are thought to promote fat loss by increasing metabolism or reducing appetite.
Recovery
Peptides like BPC-157 and TB-500 are believed to enhance recovery by promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation, potentially allowing for more frequent and intense workouts.
Endurance
Some peptides, such as erythropoietin (EPO) mimetics, are thought to increase red blood cell production, leading to improved endurance and performance during workouts.
Injury Prevention
Peptides like collagen peptides are believed to support joint and connective tissue health, potentially reducing the risk of injuries associated with intense training.
In this section, we will provide you with a list of FDA-approved peptides that are commonly used by bodybuilders.
Growth Hormone Releasing Peptides (GHRPs)
GHRPs stimulate the release of growth hormone, promoting muscle growth and recovery. FDA-approved GHRPs include: - Tesamorelin (Egrifta) - Sermorelin (Geref)
Growth Hormone Secretagogues (GHSs)
GHSs also stimulate the release of growth hormone and offer potential benefits for bodybuilders. An FDA-approved GHS is: - Macimorelin (Macrilen)
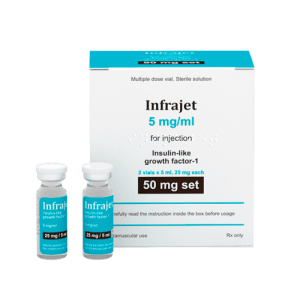
Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) Peptides
IGF-1 plays a vital role in muscle development and repair. One FDA-approved IGF-1 peptide is: - Mecasermin rinfabate (Increlex)
4. Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Analogs
These peptides regulate hormone levels in the body, impacting muscle growth and performance. An FDA-approved analog is: - Leuprolide acetate (Lupron Depot) Thank you for providing information on various growth hormone-related peptides and analogs.
Tesamorelin (Egrifta)
Tesamorelin is a growth hormone-releasing peptide that has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of HIV-associated lipodystrophy. It stimulates the release of growth hormone, which can promote muscle growth and aid in recovery.
Sermorelin (Geref)
Sermorelin is another FDA-approved growth hormone-releasing peptide that stimulates the production and release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. It may be used to treat children with growth hormone deficiency or adults with low levels of growth hormone.
Macimorelin (Macrilen)
Macimorelin is a Growth Hormone Secretagogue (GHS) that received FDA approval for diagnosing Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency (AGHD). GHSs like macimorelin stimulate the release of growth hormones from the pituitary gland, aiding in muscle development.
4. Mecasermin rinfabate (Increlex)
Mecasermin rinfabate is an insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) peptide approved by the FDA for treating children with short stature due to severe primary IGF-1 deficiency or IGF-1 gene deletion mutations. IGF-1 plays a crucial role in promoting muscle development and repair.
Leuprolide acetate (Lupron Depot)
While not strictly categorized as a peptide, leuprolide acetate belongs to a class called Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone Analogs, which regulate hormonal levels in both males and females by suppressing sex hormones such as testosterone or estrogen. This regulation can indirectly impact muscle growth and performance. It's important to note that these substances are only available under prescription and should always be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
It's important to note that while these peptides are FDA-approved for specific medical conditions, their off-label use for bodybuilding purposes may not be explicitly endorsed by regulatory authorities.
Before incorporating any peptide into your fitness regimen, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in sports medicine or endocrinology to ensure safe usage and proper dosing.
Remember that achieving optimal results in bodybuilding requires a comprehensive approach involving proper nutrition, training, rest, and guidance from qualified professionals.
HGH Frag 176-191
This peptide is known for its fat-burning. It is specifically designed to target and break down fat cells, helping individuals achieve a leaner physique while preserving muscle mass.
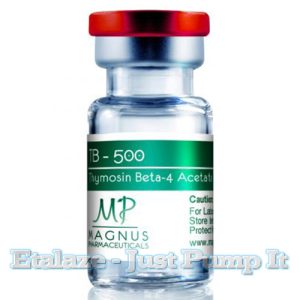
TB-500
It is widely used for its ability to promote healing and recovery from injuries, making it a valuable asset for athletes engaged in intense training regimens.
Must Read: Horse Chestnut and Other Supplements to Get Rid of Water Retention
IGF1 LR3
This peptide stimulates muscle cell growth, leading to increased muscle mass and improved recovery time.
The peptide works as a protein hormone and contains a very unique chemical structure.
Additionally, LR3 it is the same as a natural insulin hormone (IGF-1) found in the liver and pancreas.
This makes it good in stimulating several natural processes such cellular growth and differentiation. For this reason, it ranks among the highest for bodybuilders who want to grow muscle.
Again, IGF1 LR3 promotes the development of Growth Hormone (GH).
Growth hormone (GH) is needed for muscle growth and development but it is usually less abundant with age.
The peptide is a synthetic (long-form) version and is mostly more potent than the standard Insulin-like Growth Factor (IGF-1).
However, most experts are of the opinion that it's not as powerful as Human Growth Hormone (HGH) supplements.
Overall, IGF1 LR3 does not come withe nasty side effects and long-term health risks compared to most performance-enhancing substances.
GHRP-6
Known for its appetite-stimulating effects, GHRP-6 also boosts growth hormone secretion, promoting muscle growth and aiding in recovery.
Melanotan II
While not directly related to muscle growth, Melanotan II is often used by bodybuilders for its tanning effects, giving them a more defined appearance on stage.
Why the FDA Takes Longer to Approve Peptides
The FDA's approval process for peptides used by bodybuilders involves ensuring safety and efficacy. Peptides, often used for muscle building, can carry risks such as side effects and long-term health consequences. Therefore, comprehensive studies on their safety, dosage, and effectiveness are required.
Many peptides used by bodybuilders may lack sufficient research or have potential adverse effects, leading to their non-approval. Additionally, some peptides may be considered performance-enhancing drugs, raising concerns about fair competition and ethical use in sports. Overall, the FDA prioritizes public health and safety in its approval process, which may limit the approval of peptides for bodybuilding purposes.
Let's delve deeper into why the FDA doesn't readily approve most peptides for bodybuilding:
Safety Concerns
Peptides can affect various bodily processes and systems. The FDA requires thorough testing to ensure they don't pose significant risks to users. This includes assessing potential side effects, interactions with other substances, and any long-term health implications.
Efficacy and Dosage
To gain FDA approval, a substance must demonstrate not only safety but also effectiveness for its intended use. This requires extensive clinical trials to establish the optimal dosage, duration of use, and expected outcomes. Many peptides used by bodybuilders may lack sufficient data on these parameters.
Regulatory Compliance
Peptides marketed for bodybuilding often fall into a regulatory gray area. If they're marketed as supplements rather than drugs, they may not undergo the same rigorous testing and oversight as pharmaceuticals. However, the FDA still expects manufacturers to comply with regulations regarding labeling, advertising claims, and quality control.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Some peptides used by bodybuilders may be considered performance-enhancing drugs, especially if they provide an unfair advantage in sports competitions. The FDA must consider the ethical implications of approving substances that could potentially undermine fair play and jeopardize athlete health.
Limited Research
Peptides used in bodybuilding may not have undergone sufficient scientific scrutiny. Many are relatively new compounds with limited research on their safety and efficacy, making it challenging for the FDA to evaluate their benefits and risks accurately.
Off-Label Use
Even if a peptide is FDA-approved for certain medical conditions, using it off-label for bodybuilding purposes may not be supported by sufficient evidence. The FDA encourages healthcare providers and consumers to use approved drugs only for their intended purposes to ensure safety and effectiveness.
In summary, the FDA's cautious approach to approving peptides for bodybuilding reflects its commitment to protecting public health and promoting evidence-based medicine. While some peptides may eventually receive FDA approval for specific uses, rigorous scientific research and regulatory oversight are essential to ensure their safety and efficacy.
Overall
When it comes to finding FDA-approved peptides for bodybuilding purposes, it is crucial to prioritize safety and legality. While there are numerous online sources claiming to offer the best FDA-approved peptides, it is important to exercise caution and do thorough research before making a purchase.
One reliable option for obtaining FDA-approved peptides is through licensed pharmacies or medical professionals. These reputable sources ensure that the peptides they provide meet the necessary quality standards and comply with FDA regulations.
Another avenue worth exploring is reputable online peptide retailers that have established a strong reputation in the industry. It is essential to look for websites that clearly state their commitment to providing FDA-approved peptides and have positive customer reviews attesting to their legitimacy.
It's important to note that purchasing peptides for bodybuilding purposes may require a prescription, depending on your location and specific regulations. Consulting with a healthcare professional or an expert in the field can provide valuable guidance on where to safely obtain FDA-approved peptides tailored to your needs.
Visit etalaze.to today and get the best offer on various peptides and supplements.
Don't Miss: YouTube Fitness Influencers to Subscribe to Right Now
Anabolic Steroids
Legality of Anabolic Steroids In Latin America

Steroids have become a prevalent topic in the context of Latin America. The use and availability of steroid products in this region have gained attention from both athletes and bodybuilders. However, it is important to approach this subject with caution and prioritize safety.
What's Special About Legal Steroids?
Legal steroids are formulated using natural ingredients that mimic the effects of traditional anabolic steroids without the harmful side effects. They are designed to promote muscle growth, increase strength, improve endurance, and enhance overall athletic performance.
Who Mostly Uses Steroids In Latin America?
In South America, individuals from various backgrounds including bodybuilders, athletes, and fitness enthusiasts are turning to legal steroids as a way to achieve their fitness goals safely. These products are widely available both online and in local supplement stores throughout the region. Legal steroids have gained popularity among individuals in South America who are looking to enhance their fitness performance safely.
These products cater to a diverse range of people, including bodybuilders, athletes, and fitness enthusiasts. The availability of legal steroids has increased both online and in local supplement stores across the region.
Must Read: Your Guide to Become A Successful Personal Trainer
Safety of Steroids
As mentioned, Legal steroids are formulated using natural ingredients that aim to mimic the effects of traditional anabolic steroids without the associated health risks. They typically contain a combination of plant extracts, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids that can support muscle growth, increase strength and endurance, and improve overall athletic performance.
One advantage of legal steroids is that they do not require a prescription or medical supervision for purchase. This accessibility has made them popular among individuals who want to improve their physique or athletic abilities but prefer a safer alternative to traditional anabolic steroids.
Reputatable Steroid Sources In Latin America
When purchasing legal steroids online or from local stores in South America, it is essential to ensure they come from reputable sources. It's also important to follow recommended dosages and consult with healthcare professionals if you have any underlying health conditions or concerns.
Remember that while legal steroids can be effective tools for enhancing fitness goals safely when used responsibly as part of a well-rounded training program and healthy lifestyle choices such as proper nutrition and adequate rest are equally crucial for achieving optimal results. Always prioritize your safety by educating yourself about the product's ingredients, potential side effects, and consulting with professionals if needed before incorporating legal steroid use into your fitness routine.
Latin America Steroid Black Market is Booming
Latin America offers a wide range of steroid products, with various brands and types available on the market. It is crucial to note that the use of steroids should always be done under medical supervision and in accordance with legal regulations.
Unfortunately most steroids are from the black market and pose serious health risks. For those interested in exploring the world of steroids, it is essential to educate oneself about the potential risks and benefits associated with their usage. Consulting a healthcare professional or expert in the field can provide valuable insights on which steroids may be suitable for individual needs. and goals. When it comes to purchasing steroids in Latin America, it is important to understand that regulations and availability may vary from country to country.
It is always advisable to do thorough research and ensure that the products you are interested in are legal and approved for use in your specific location. There are numerous reputable brands offering high-quality steroid products in Latin America. These brands prioritize safety, efficacy, and quality control throughout their manufacturing processes.
Your Brand of Choice Matters
By choosing well-established brands, you can have peace of mind knowing that you are purchasing reliable products. When it comes to purchasing steroid products in Latin America, it's crucial to prioritize your safety and well-being. That's why opting for reputable brands is essential. These brands have built a strong reputation by placing a high emphasis on safety, efficacy, and quality control throughout their manufacturing processes.
Moreover, reputable brands often invest in research and development to continuously improve their formulations, ensuring optimal results for users. They understand the unique needs of individuals looking for steroid products and strive to provide safe options that deliver the desired effects.
When selecting a brand, consider factors such as customer reviews, certifications or accreditations from regulatory bodies or independent testing organizations. This information will further validate their commitment to producing safe and effective products. Remember, your health is paramount when considering using some steroid products. So always choose reputable brands that prioritize safety, efficacy, and quality control throughout their manufacturing processes in Latin America.
Which Steroids Are You Likely to Come Across?
Countries such as Brazil are known for its thriving fitness and bodybuilding culture, and as such, the use of anabolic steroids is prevalent in the country. In this section, we will explore some of the commonly used types of anabolic steroids in Latin America.
1. Testosterone Enanthate: This is one of the most widely used anabolic steroids in Brazil. It is a synthetic version of testosterone and helps to increase muscle mass and strength.
2. Deca Durabolin (Nandrolone Decanoate): Another popular choice among Brazilian bodybuilders, Deca Durabolin promotes muscle growth, improves endurance, and aids in recovery.
3. Dianabol (Methandrostenolone): Dianabol is known for its rapid muscle-building effects. It increases protein synthesis and nitrogen retention in the muscles, leading to significant gains in size and strength.
4. Stanozolol: Also known as Winstrol, Stanozolol is favored by athletes looking to enhance performance without excessive weight gain. It helps improve speed, agility, and overall athletic performance.
5. Trenbolone: Trenbolone is a powerful steroid that promotes lean muscle mass while reducing body fat. It also enhances strength and endurance levels.
6. Anadrol (Oxymetholone): Anadrol is highly regarded for its ability to rapidly increase muscle size and strength. It also improves red blood cell production, leading to enhanced oxygen delivery to muscles during intense workouts.
Don't Miss: Using SARMs on Top of a Steroid Cycle: DOs and DON’Ts
10. Anadrol (Oxymetholone) is highly regarded for its ability to rapidly increase muscle size and strength. It works by improving red blood cell production, leading to enhanced oxygen delivery to muscles during intense workouts. This allows users to push through plateaus and achieve greater gains in their training sessions. It's important to note that the use of these steroids should only be done under proper medical supervision or guidance from a healthcare professional.
Additional Tips to Buy Steroids in Latin America
Misuse or abuse of illegal steroids can lead to serious health complications.
In South America, the use and availability of anabolic steroids vary across different countries. While it is important to note that the use of steroids without a valid prescription is illegal in many places, including South American countries, it is still necessary to understand the prevalence and accessibility of these substances.
Argentina
In Argentina, anabolic steroids are known to be available on the black market. Despite efforts by authorities to crack down on their distribution, they continue to be used by some individuals for performance enhancement purposes.
Colombia
Colombia has also seen a presence of anabolic steroids within its borders. Similar to Argentina, they are often obtained through illicit means. The country has implemented measures to combat their distribution and usage but challenges persist.
Chile
Chile has reported cases of illegal steroid use as well. Authorities in Chile have taken steps to regulate and control the distribution of these substances, aiming to mitigate their misuse and potential health risks.
Cuba
Cuba has strict regulations regarding anabolic steroids. They are classified as controlled substances and can only be obtained with a valid medical prescription from authorized healthcare professionals.
Other Latin America Countries
In Uruguay, Paraguay, and Bolivia, anabolic steroids are also subject to strict regulations. Their sale and use without proper medical supervision are prohibited by law.
Overall
Individuals in these countries are seeking safe and effective alternatives to traditional anabolic steroids. These Latin steroids are gaining traction in every South American country, offering fitness enthusiasts and athletes a legal and regulated option for enhancing their performance. Lastly, If you're looking for legit steroids for various fitness goals etalaze.biz is the ultimate online store. Visit them today to get a range of steroid products and supplements at good, discounted rates.
Related Article: 10 Famous Bodybuilders Who Died in the Line of Duty and Why
-

 Bodybuilding2 years ago
Bodybuilding2 years agoNew Arrival Workout Equipment on Amazon for The Disabled
-

 Steroids2 years ago
Steroids2 years agoSupplemental Breast Milk for Bodybuilders: The Secret Behind It
-

 Steroids2 years ago
Steroids2 years agoDwarf Bodybuilders Giving Pros A Run for Their Money
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoVOX Testing: Why Bodybuilders Must Have It Tested Regularly
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoShavers and Other Body Grooming Equipment for Bodybuilders In 2023
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoChatGPT and Other Avenues to Find Great Bodybuilding Coaches
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoBest Oil Recommendations Before Competition for Subtle Shimmer
-

 Steroids1 year ago
Steroids1 year agoPowerlifting Vs Power Building: Find Out the Big Difference and When to Shift Between the Two
-

 Beginners12 months ago
Beginners12 months agoTren Cycle for Beginners
-

 Bodybuilding11 months ago
Bodybuilding11 months agoCompetition Prep Cycle for Pro Bodybuilders
-

 Nutrition9 months ago
Nutrition9 months agoEverything Nutritional Food: What’s Too Much Or Too Little
-

 Anabolic Steroids8 months ago
Anabolic Steroids8 months agoLegality of Anabolic Steroids In Latin America
-

 Bodybuilding8 months ago
Bodybuilding8 months agoChia Seeds in A Bodybuilder’s Diet: An Expert’s Advice
-
 Bodybuilding6 months ago
Bodybuilding6 months agoList of FDA-Approved Peptides
-

 Anabolic Steroids7 months ago
Anabolic Steroids7 months agoStart The New Year Strong With These Tips
-

 Anabolic Steroids9 months ago
Anabolic Steroids9 months agoNatural Steroids for Bodybuilding
-

 Beginners9 months ago
Beginners9 months agoCalisthenics: Secret to Building A Better Upper and Middle Body
-

 Bodybuilding7 months ago
Bodybuilding7 months agoUnique Things That Have Redefined Mr Olympia Over The Years
-

 Steroids5 months ago
Steroids5 months agoTrenbolone: Why it Remains A Beast In the Market
-

 Bodybuilding Products4 months ago
Bodybuilding Products4 months agoTelmisartan In Bodybuilding: An Expert’s Advice
-
 Bodybuilding5 months ago
Bodybuilding5 months agoThe Importance of Scaptions in Female Athletes
-

 Bodybuilding4 months ago
Bodybuilding4 months agoHow Much Is Too Much Cardio? Understanding Heart Rate Zones
-

 Bodybuilding6 months ago
Bodybuilding6 months agoFunny Gym Stories and Moments to Light Up Your Day
-

 Steroids8 months ago
Steroids8 months agoThese Bodybuilding Equipment Might Become Obsolete Next Year (See Alternative Upgrades)
-

 Bodybuilding7 months ago
Bodybuilding7 months agoCalorie Dumping: A Bodybuilder’s Guide












 Buy Now
Buy Now